Welcome to the AWS Quick Start Guide: Back Up Your Files to Amazon Simple Storage Service. You can use Amazon S3 to store and retrieve any amount of data at any time, from anywhere on the web. By completing the steps in this quick start guide, you will successfully create a new S3 bucket, add a file to it, retrieve this file, and finally delete it, all within the AWS Free Tier.
In order to complete this quick start guide, you must have an Amazon Web Services (AWS) account. When you sign up for AWS, your AWS account is automatically signed up for all services in AWS, including Amazon S3. If you don’t have an AWS account, use the following procedure to create one.
To sign up for AWS
1. Open https://portal.aws.amazon.com/billing/signup.
2. Follow the online instructions.
Part of the sign-up procedure involves receiving a phone call and entering a verification code on the phone keypad.
When you sign up for an AWS account, an AWS account root user is created. The root user has access to all AWS services and resources in the account. As a security best practice, assign administrative access to a user, and use only the root user to perform tasks that require root user access.
For more information about Amazon S3, see the Amazon Simple Storage Service Documentation.
Step 1: Create an Amazon S3 Bucket
First, you need to create an Amazon S3 bucket where you will store your objects.
1. Sign in to the preview version of the AWS Management Console.
2. Under Storage & Content Delivery, choose S3 to open the Amazon S3 console.
If you are using the Show All Services view, your screen looks like this
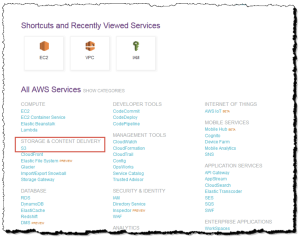
If you are using the Show Categories view, your screen looks like this with Storage Content Delivery expanded:
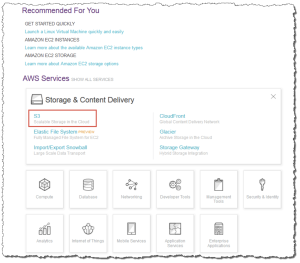
3. From the Amazon S3 console dashboard, choose Create Bucket.
4. In Create a Bucket, type a bucket name in Bucket Name.
The bucket name you choose must be globally unique across all existing bucket names in Amazon S3 (that is, across all AWS customers). For more information, see Bucket Restrictions and Limitations.
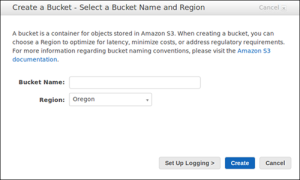
5. In Region, select the Region you want your bucket to be created in. Choose Jakarta.
6. Choose Create.
When Amazon S3 successfully creates your bucket, the console displays your empty bucket in the Buckets pane.
Step 2: Upload a File to Your Amazon S3 Bucket
Now that you’ve created a bucket, you’re ready to add an object to it. An object can be any kind of file: a document, a photo, a video, a music file, or other file type.
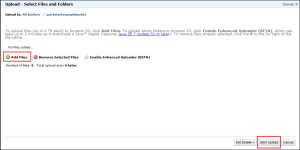
1. In the Amazon S3 console, choose the bucket where you want to upload an object, choose Upload, and then choose Add Files.

2. In the file selection dialog box, find the file that you want to upload, choose it, choose Open, and then choose Start Upload.
You can watch the progress of the upload in the Transfer pane.
Step 3: Retrieve a File from Your Amazon S3 Bucket
Now that you’ve added an object to a bucket, you can open and view it in a browser. You can also download the object to your local computer.
1. In the Amazon S3 console, choose your S3 bucket, choose the file that you want to open or download, choose Actions, and then choose Open or Download.
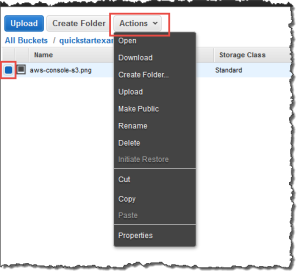
2. If you are downloading an object, specify where you want to save it.
The procedure for saving the object depends on the browser and operating system that you are using.
Step 4: Delete a File From Your Amazon S3 Bucket
If you no longer need to store the file you’ve uploaded to your Amazon S3 bucket, you can delete it.
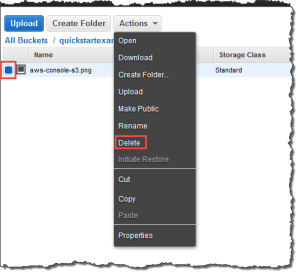
Within your S3 bucket, select the file that you want to delete, choose Actions, and then choose Delete. In the confirmation message, choose OK.
Credit to: AWS Documentation




